Eczema and the Gut–Skin Axis: What’s the Link?
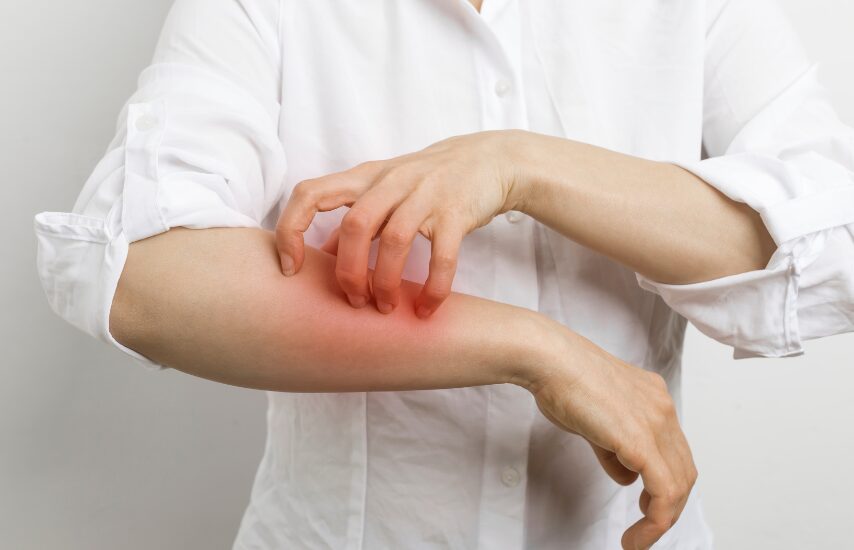
Eczema (atopic dermatitis) affects millions globally, causing skin inflammation, dryness, and frequent flare-ups. While topical treatments and allergen-avoidance remain central, an emerging body of research points to another influential factor in skin health: the gut. The concept of the gut–skin axis proposes that gut microbes, immune signalling and barrier-function in the digestive system can affect skin condition. This allows us to ask: could improving gut health be a meaningful part of managing eczema?

How the Gut–Skin Axis Works: The Hidden Connection
Your gut and skin are connected not just by circulation, but through immune pathways, microbial metabolites, and barrier integrity. The gut microbiome — the trillions of bacteria in your digestion system — produces compounds like short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and modulates immune responses which in turn influence skin health. A comprehensive review titled “Unraveling the Gut–Skin Axis: The Role of Microbiota in Skin Health and Disease” found that dysbiosis (microbial imbalance) in the gut is implicated in dermatological disorders ranging from acne to eczema.
Gut barrier disturbances allow microbial by-products to leak into circulation, triggering systemic inflammation which can manifest as skin barrier dysfunction or flare-ups. In short: skin symptoms may reflect what’s happening deeper in your gut.
Evidence Linking Gut Health and Eczema
Several studies provide concrete evidence linking gut microbiome changes with eczema severity and incidence. For example, a randomized controlled trial titled “Efficacy of a Probiotic Supplement in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis” found that adult eczema patients taking a probiotic supplement (strains L. plantarum, L. reuteri, L. rhamnosus) over 56 days showed improvements in skin smoothness, hydration, and reductions in inflammatory skin-markers.
In addition, a 2022 meta-analysis, “The Role of Probiotics in the Treatment of Adult Atopic Dermatitis”, reviewed six RCTs (241 adult participants) and found significant reductions in SCORAD (a measure of eczema severity) with probiotic use.
These findings support the idea that interventions targeting the gut may help reduce skin inflammation and improve eczema outcomes.
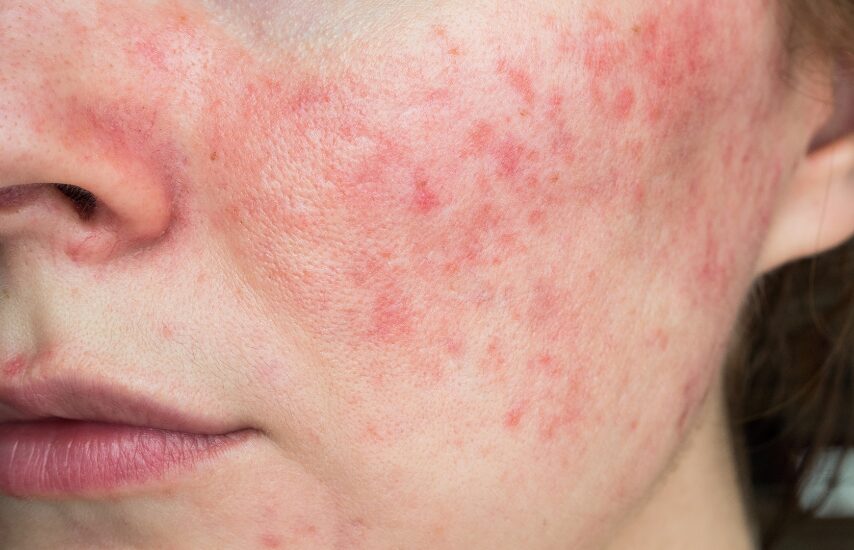
Why Gut Imbalance Might Trigger Flare-ups
The mechanisms behind the gut–skin connection in eczema are still being explored, but several pathways appear important:
- Intestinal permeability (“leaky gut”): When the gut barrier is compromised, microbial components (LPS, toxins) can enter the bloodstream and trigger systemic inflammation.
- Immune dysregulation: Gut microbial imbalance can shift immune response toward inflammation (e.g., Th2-dominance) which is central to eczema’s pathology.
- Reduced beneficial microbial metabolites: Healthy microbes produce SCFAs that regulate inflammation and support barrier-function. When these are low, vulnerability increases.
- Stress and endocrine influence: Gut microbes influence cortisol and other hormonal pathways; high stress and hormonal imbalance can worsen both gut and skin health.
Together, these mechanisms help explain why people with eczema often also display digestive symptoms, allergies, or other immune-related conditions.
How to Support Gut Health for Better Skin
If the gut–skin axis is real, then optimising gut health becomes a therapeutic strategy. Here are evidence-based steps:
1. Diversify your diet. Eat plenty of fibre-rich plants, legumes, whole grains. These foods feed beneficial gut bacteria and support SCFA production.

2. Incorporate fermented foods & targeted probiotics. Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and probiotic supplements can help rebalance the microbiome.
3. Reduce processed foods and high sugar. Ultra-processed items and high sugar diets correlate with poorer microbial diversity and more inflammation.
4. Manage stress and get adequate sleep. Psychological stress and sleep disruption both negatively affect the microbiome and barrier integrity.
5. Explore specialised probiotic interventions. Recent clinical evidence supports probiotic use in eczema; working with a specialist or selecting products from trusted brands can help. At Bioma Health we emphasise research-backed probiotic support as part of a gut-skin strategy.
The Role of Bioma Health in Gut–Skin Support
At Bioma Health we recognise that managing eczema requires more than creams and avoidance. By focusing on the gut-microbiome and its influence on immune and skin health, we help you build foundational support. Whether through high-quality probiotics, gut-friendly nutrition plans, or barrier-supporting lifestyle recommendations, our approach aims to strengthen the gut so your skin can reflect that internal resilience.
Healing From the Inside Out
The gut–skin connection challenges the idea that skin disorders can be treated in isolation. Instead, your gut health, immune system, and skin barrier are part of one integrated ecosystem. By supporting your microbiome and gut integrity, you give your skin a better chance of healing and maintaining health.
Related articles




